Identification of putative dental epithelial stem cells in a lizard with life-long tooth replacement.
Authors: Gregory R. Handrigan, Kelvin J. Leung and Joy M. Richman. Lab of Joy Richman, Cell & Developmental Biology (CELL) Research Group, Department of Dentistry
Published in Development November 1, 2010 137, 3545-3549. doi: 10.1242/dev.052415
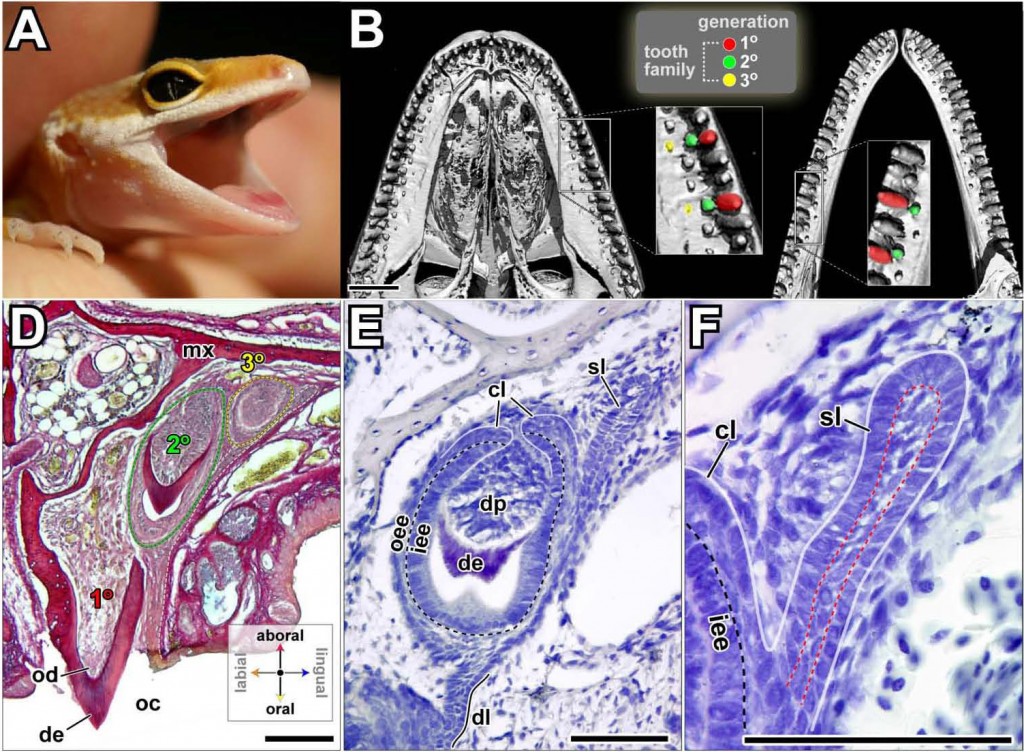
Abstract: Most dentate vertebrates, including humans, replace their teeth and yet the process is poorly understood. Here, we investigate whether dental epithelial stem cells exist in a polyphyodont species, the leopard gecko (Eublepharis macularius). Since the gecko dental epithelium lacks a histologically distinct site for stem cells analogous to the mammalian hair follicle bulge, we performed a pulse-chase experiment on juvenile geckos to identify label-retaining cells (LRCs). We detected LRCs exclusively on the lingual side of the dental lamina, which exhibits low proliferation rates and is not involved in tooth morphogenesis. Lingual LRCs were organized into pockets of high density close to the successional lamina. A subset of the LRCs expresses Lgr5 and other genes that are markers of adult stem cells in mammals. Also similar to mammalian stem cells, the LRCs appear to proliferate in response to gain of function of the canonical Wnt pathway. We suggest that the LRCs in the lingual dental lamina represent a population of stem cells, the immediate descendents of which form the successional lamina and, ultimately, the replacement teeth in the gecko. Furthermore, their location on the non-tooth-forming side of the dental lamina implies that dental stem cells are sequestered from signals that might otherwise induce them to differentiate.




